In this Python Dictionaries article we want to learn about Understanding Basics of Python Dictionaries, so Python dictionaries are a type of collection that allows you to store key value pairs. they are similar to lists but instead of being indexed by numerical index like lists, they are indexed by keys, which can be of any hashable data type such as strings, integers or tuples.
Understanding Basics of Python Dictionaries
For creating a dictionary in Python, you can use curly braces {} or builtin dict() function.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
# using curly braces my_dict = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'} # using dict() function my_dict = dict(key1='value1', key2='value2') |
For accessing values in a dictionary, you can use the key inside square brackets [].
|
1 2 3 |
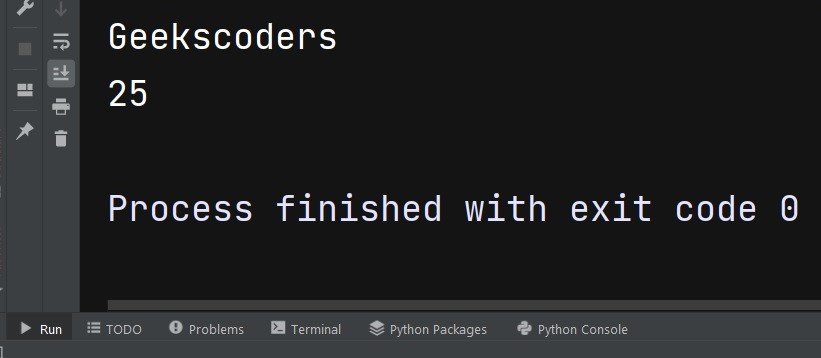
my_dict = {'name': 'Geekscoders', 'age': 25, 'city': 'New York'} print(my_dict['name']) print(my_dict['age']) |
This will be the result
If you try to access a key that doesn’t exists, you will get KeyError. to avoid this error you can use get() method, which returns None if the key doesn’t exist, or default value if specified.
|
1 2 3 4 |
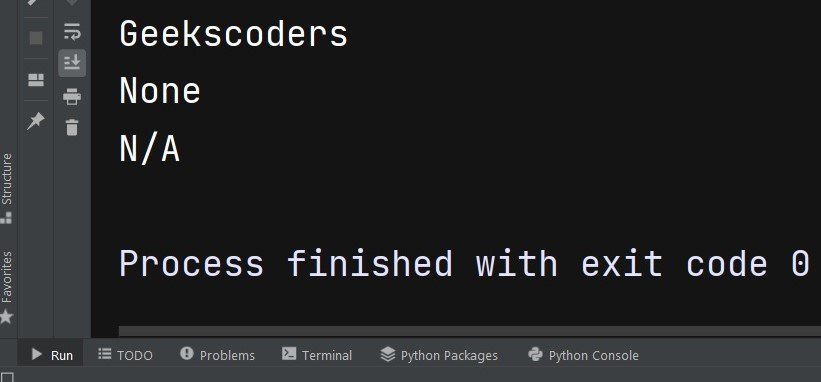
my_dict = {'name': 'Geekscoders', 'age': 25, 'city': 'New York'} print(my_dict.get('name')) print(my_dict.get('gender')) print(my_dict.get('gender', 'N/A')) |
This will be the result
Also you can add new item or modify an existing one in a dictionary, you can use the key inside square brackets [] and assign value to it.
|
1 2 3 4 |
my_dict = {'name': 'Geekscoders', 'age': 25, 'city': 'New York'} my_dict['name'] = 'Bob' my_dict['gender'] = 'Male' print(my_dict) |
To remove an item from a dictionary, you can use the del keyword followed by the key.
|
1 2 3 |
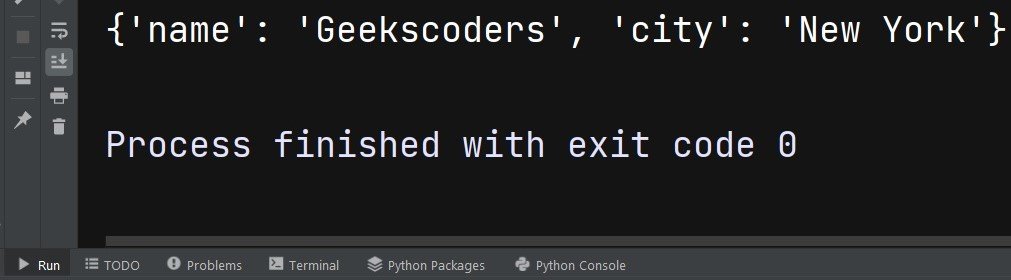
my_dict = {'name': 'Geekscoders', 'age': 25, 'city': 'New York'} del my_dict['age'] print(my_dict) |
This will be the result and the age is removed
Also you can loop through a dictionary, you can use for loop. by default loop will iterate over the keys of the dictionary.
|
1 2 3 |
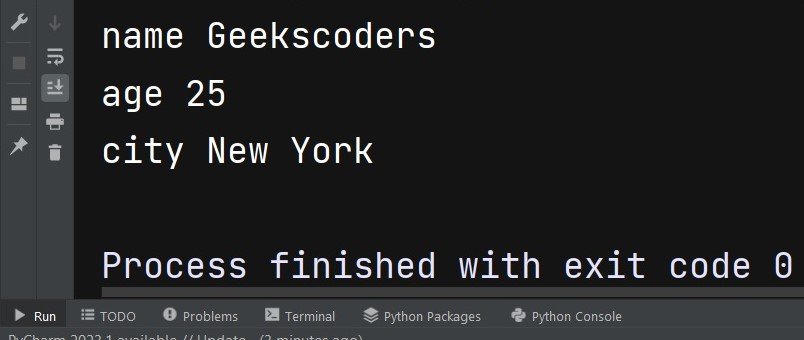
my_dict = {'name': 'Geekscoders', 'age': 25, 'city': 'New York'} for key in my_dict: print(key, my_dict[key]) |
This is the result
You can also use the items() method to loop over both the keys and values of the dictionary.
|
1 2 3 |
my_dict = {'name': 'Geekscoders', 'age': 25, 'city': 'New York'} for key, value in my_dict.items(): print(key, value) |
