In this Django REST Framework lesson we are going to learn about Django REST Framework Class API View, till now we have learned some basics on django rest framework, and we have created some examples on functions based api view. now it is time to talk about class based api view in django. REST framework provides an APIView class, which subclasses Django’s View class. Using APIView class is pretty much the same as using a regular View class, as usual, the incoming request is dispatched to an appropriate handler method such as .get() or .post(). Additionally, a number of attributes may be set on the class that control various aspects of the API policy.
OK now we are going to bring some changes in our views.py file again, i have removed all of the codes from the views.py, because by using class based api view i don’t need that code.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 |
from .models import Article from .serializers import ArticleSerializer from rest_framework.views import APIView from rest_framework.response import Response from rest_framework import status class ArticleList(APIView): def get(self, request): articles = Article.objects.all() serializer = ArticleSerializer(articles, many=True) return Response(serializer.data) def post(self, request): serializer = ArticleSerializer(data=request.data) if serializer.is_valid(): serializer.save() return Response(serializer.data, status=status.HTTP_201_CREATED) return Response(serializer.errors, status=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST) class ArticleDetails(APIView): def get_object(self, id): try: return Article.objects.get(id=id) except Article.DoesNotExist: return Response(status=status.HTTP_404_NOT_FOUND) def get(self, request, id): article = self.get_object(id) serializer = ArticleSerializer(article) return Response(serializer.data) def put(self, request,id): article = self.get_object(id) serializer = ArticleSerializer(article, data=request.data) if serializer.is_valid(): serializer.save() return Response(serializer.data) return Response(serializer.errors, status=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST) def delete(self, request, id): article = self.get_object(id) article.delete() return Response(status=status.HTTP_204_NO_CONTENT) |
Also you need to bring changes in your urls.py file , because now we are using class based views.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
from django.urls import path from .views import ArticleList, ArticleDetails urlpatterns = [ path('articles/', ArticleList.as_view()), path('articles/<int:id>/', ArticleDetails.as_view()) ] |
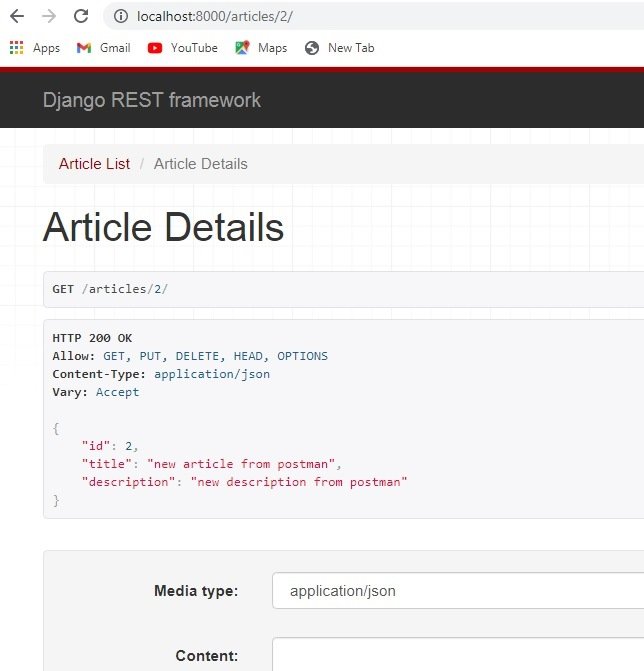
If you go to http://localhost:8000/articles/ you can see a browsable api from the django rest framework with same functionality of posting article, getting article, retrieving article, deleting article and updating article . but this time we have used class based api view.