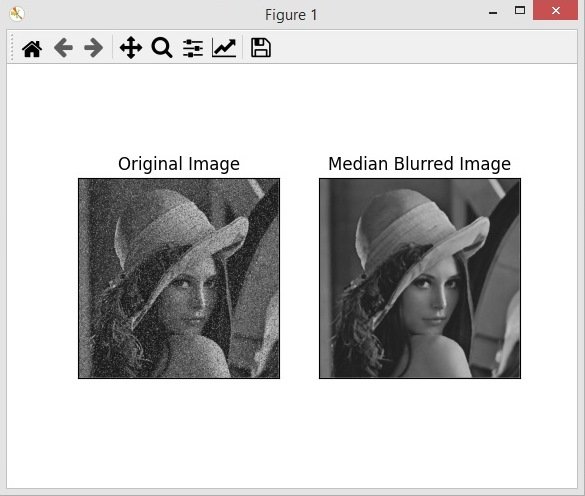
In this Python OpenCV lesson we are going to learn about Python OpenCV Median Blurring, Median Blurring computes the median of all pixels under the kernel and the central pixel is replaced with the median value, according to OpenCV Documentation it is mostly used for removing salt and pepper noises.
This is the complete code for this lesson.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
import cv2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #read the image in opencv image = cv2.imread('lena_salt.png') #create medianBlur function median = cv2.medianBlur(image,5) #convert the image from bgr to rgb original_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) median_blur = cv2.cvtColor(median, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) #show the image using matplotlib plt.subplot(121) plt.imshow(original_image),plt.title('Original Image') plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) plt.subplot(122),plt.imshow(median_blur),plt.title('Median Blurred Image') plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) plt.show() cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows() |
For this purpose we are going to use this image, you can see that we have a lot of noises in this image.

So in here we are going to use cv2.medianBlur() function for this purpose, we need to add some parameters, our image and also the kernel size.
|
1 |
median = cv2.medianBlur(image,5) |
Because we are going to show our image in Matplotlib, so Matplotlib uses RGB (Red, Green, Blue) color system, and OpenCV uses BGR (Blue, Green, Red) color system, we need to convert the BGR color to RGB. if we don’t do this there will be messed up in the color.
|
1 2 |
original_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) median_blur = cv2.cvtColor(median, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) |
Run the complete code and this is the result.